|
BOOK NOW |
ASK ABOUT YOUR PAIN |
Home > Blog > Hand Therapy & Customized Splinting > Finger, Hand, Wrist, Forearm & Elbow Conditions > De Quervain's Tenosynovitis
De Quervain's Tenosynovitis
Physiotherapy & Hand Therapy
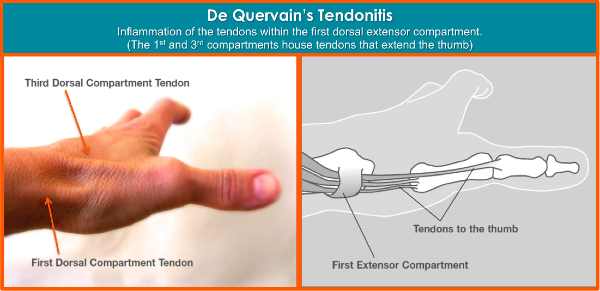
De Quervain's tenosynovitis is also commonly known as
- washerwoman's sprain
- mummy thumb
- de Quervain's tendinosis of the sheath
- blackberry thumb
- radial styloid
tenosynovitis and
- de Quervain's disease
It is basically a tendinosis of the tendon sheath (cover) that wraps around the two tendons of the thumb, the extensor pollicis longus (EPL) and the abductor pollicis brevis (APB).
How does de Quervain's tenosynovitis happen?
So the two tendons as mentioned above, the EPL and APB tendons run alongside each other, and have closely and related functions:
- which is to move the thumb away from the hand by
extension (like how you signal "good" with your thumb)
and/or
- abduction (make a "C" or an "O" of your thumb and fingers).
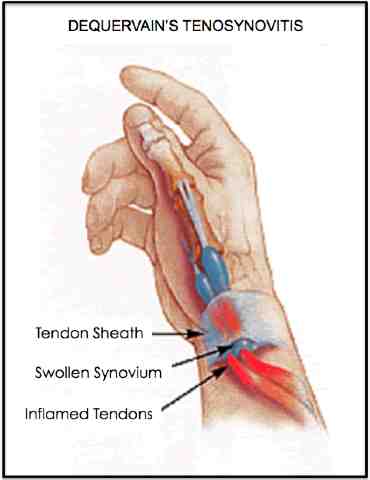
What happens is that these tendons run through a synovial sheath (imagine it to be like a blanket that wraps around the tendons) which contains them. Due to repetitive motion, this synovial sheath slowly over time and damage, thickens and degenerates, causing inflammation, swelling and pain).
De Quervain tenosynovitis is also commonly seen in new mothers and fathers, as they often lift up and put down their newborn babies by holding the babies under their armpits BUT studies show that De Quervains is more common in women as their wrists have a greater angle at the greater styloid process, causing a higher level of stress for the APB and EPL at the synovial sheath.
Causes of de Quervain's tenosynovitis
It is related directly to:
- wear and tear
- repetitive strain injury
- one's responsibilities, roles and work.
As mentioned earlier, new parents often carry and put down their new borns, causing additional strain and stress repeatedly at their wrists (and their backs).
People whose work involves a flicking of their wrists e.g. opening a can or bottle; or similarly, individuals whose work involves using a lot of screw driver will also have this injury as well.
Also, there is an association caused by the use of smartphones, which was where the term "Blackberry Thumbs" came about.
Which is basically de Quervain's tenosynovitis.
Symptoms and Testing
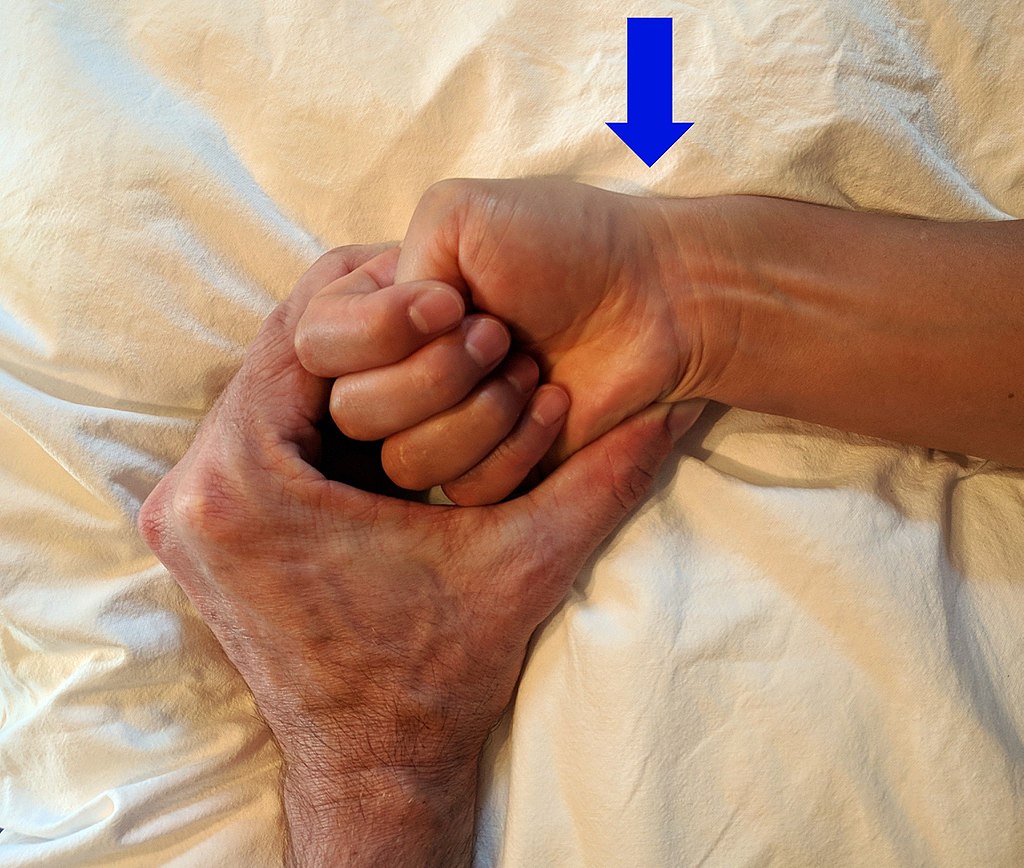
Arrow marks were the pain is worsened in DeQuervain syndrome
Main symptoms of De Quervain's tenosynovitis are
- sharp pain with thumb and wrist flexion
- tenderness at APB/EPL at wrist crease
- swelling
- difficulty using thumb in activities that involve gripping/gripping+movements
In our physiotherapy and hand clinics in Singapore, first of all we need to use the Finkelstein test to diagnose this disease.
To perform this test, we get our patients to bend their affected thumbs into the palm of their hands, close the other four fingers around the thumb, and bend their wrist downwards (see image above withthe arrow).
At any point if there is pain, there is an increased likelihood of de Quervain's - the more painful with lesser movements, the more severe.
Next we need to test for tenderness and swelling at the synovial sheath at the wrist for the EPL and APB.
Tenderness and swelling usually confirms the the De Quervain's tenosynovitis diagnosis, and it also pinpoints more acute or serious the condition is (there are mild forms and there are severe forms, where movements are locked/too painful to move).
We may also need to do differential diagnosis to rule out possible conditions such as
- wrist fractures
- osteoarthritis
- wrist sprains
- Wartenberg's syndrome
...so that we give accurate and effective hand
physiotherapy treatment for their exact hand conditions.
Physiotherapy and Hand Therapy Intervention
Surgeons and physicians will usually four types of medical/surgical solutions, based on severity and how fast patient want results:
- painkillers and anti-inflammatories
- H&L injections
- surgical "release" intervention
- non-invasive hand therapy, occupational therapy and physiotherapy for De Quervain's
For most cases of de Quervain's tenosynovitis, we will often custom make a splint to fit your hand and wrist, to immobilize the wrist and thumb at the meta-carpo-phalangeal joint (MCP level; at the thumb's knuckle) but at the same time allows your thumb end joint and other fingers to move - this is important to rest the hand and protecting it from aggravation due to
- accidental mobilization
- accidentally lifting something
- trauma such as direct hits, blows etc.
We also will provide cold therapy to decrease the amount of inflammation and swelling, decreasing the amount of pain that you may experience (pain relief). We'll combine this with retrograde massage for a synergistic pattern to drain swelling.
Ultrasound therapy will also help to accelerate the healing process of the soft tissues such as synovial sheath and tendons.
The hand therapist would then also need to determine the cause of the injury, so that we will be able to advise on any changes required to activities/exercise e.g. changing the way a task is done if the inappropriate biomechanics was used e.g. ergonomics of keyboard, usage of phone, writing etc